AGRICULTURE

Imagine being dropped onto the remote island of Andøya, Norway—Survivor style—for five days of intensive jamming and spoofing trials. This is Jammertest.
Hosted by Norwegian governmental organisations, Jammertest is a largescale, over-the-air GNSS radio frequency interference (RFI) field testing arena to facilitate industry, academia and GNSS users to develop and evaluate mitigation solutions.
With a detailed map and schedule of various RFI environments in hand, attendees are free to choose the locations and scenarios to test the mettle of their anti-jamming and anti-spoofing technologies.
Features of GNSS Resilience and Integrity Technology (GRIT) on an OEM7 receiver were tested in real-world conditions including interference monitoring and characterisation, and spoofing detection modules. Galileo navigation message authentication using a Galileo E1-B Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA). prototype was also tested.
For the OEM7 receiver, a multi-layered spoofing detection approach has been implemented, which is specifically supported by receiver design choices. OSNMA can provide another layer in that multi-layered approach; however, when it comes to spoofing detection, as shown in the Jammertest 2023 results, the OEM7 methods offer faster and more inclusive solutions across different types of spoofing attacks.
Written by Ali Broumandan, resilient GNSS lead, Ali Pirsiavash, GNSS resilience researcher, Isabelle Tremblay, geomatics designer and Sandy Kennedy, VP innovation at Hexagon’s Autonomy & Positioning division, this article highlights the jamming and spoofing detection and classification performance of OEM7 receivers, providing a detailed description of the types of spoofing attacks and detection techniques and how GRIT firmware and OSNMA fared in jamming and spoofing scenarios.
Power spectral density output of GNSS Interference Toolkit (ITK), part of GRIT under jamming (left) spoofing (right).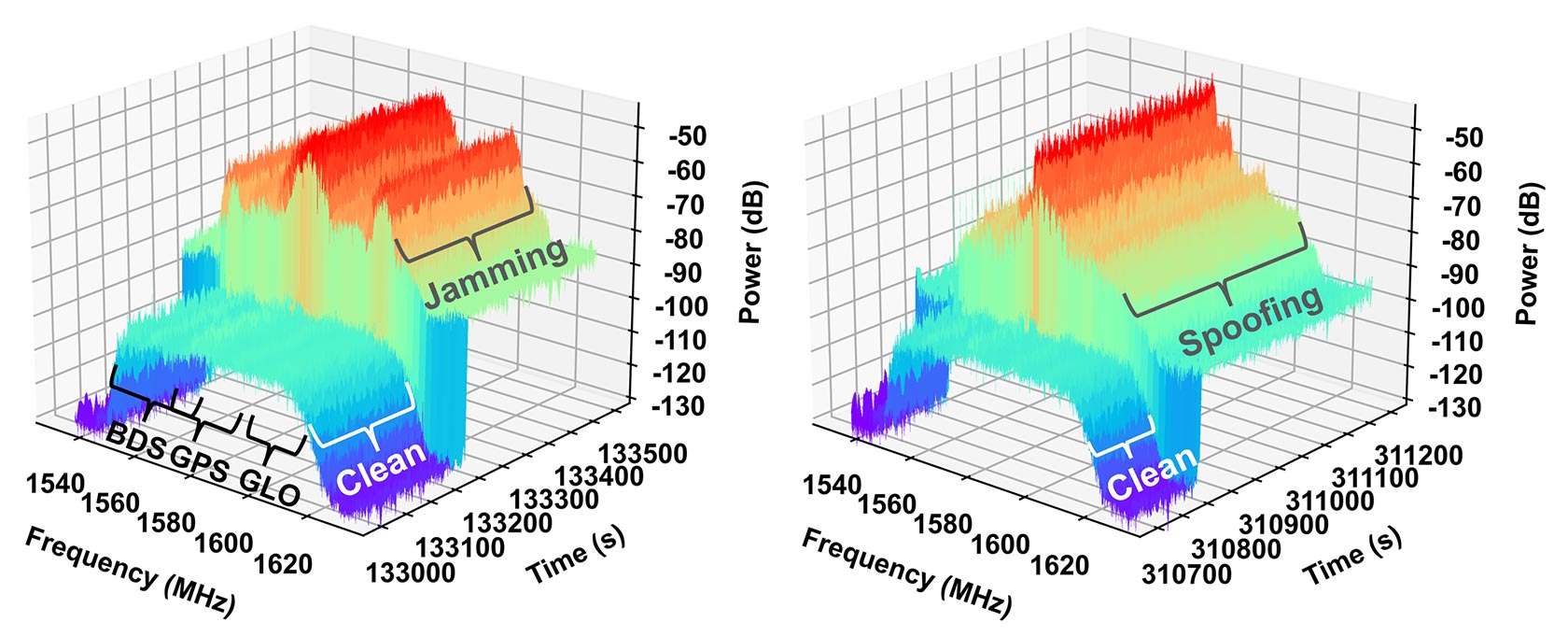
Read the full article by downloading Velocity 2024